Data automation is quietly becoming the most valuable Python skill. While everyone chases machine learning and AI, companies desperately need developers who can automate the mundane — processing spreadsheets, cleaning databases, generating reports, moving data between systems. These tasks consume thousands of hours yearly at every organization.
The good news: data automation is more accessible than advanced AI. You don’t need a PhD or years of study. With focused Python training, you can start automating real data tasks within weeks. This guide breaks down what you actually need to learn and how to build skills employers pay for. For a structured approach to these concepts, explore this comprehensive guide to Python data automation.
Why Data Automation Specifically?
Python can do almost anything — web development, games, AI, automation. So why focus on data automation?
Universal demand: Every company has data problems. Marketing teams drowning in spreadsheets. Finance departments manually copying numbers between systems. Operations staff spending hours on reports. Data automation skills apply everywhere.
Immediate value: Unlike building a new app (which might take months), a single automation script can save hours the first week you deploy it. This makes proving your value straightforward — “I saved the team 20 hours this month” is compelling.
Lower barrier to entry: You don’t need to understand distributed systems or complex algorithms. Data automation requires solid Python basics, familiarity with a few libraries, and problem-solving ability.
Career flexibility: Data automation skills fit into many roles — data analyst, business analyst, operations specialist, or dedicated automation engineer. You’re not locked into one career path.
The Core Skills You Need
Forget trying to learn everything. These specific skills cover 80% of real-world data automation:
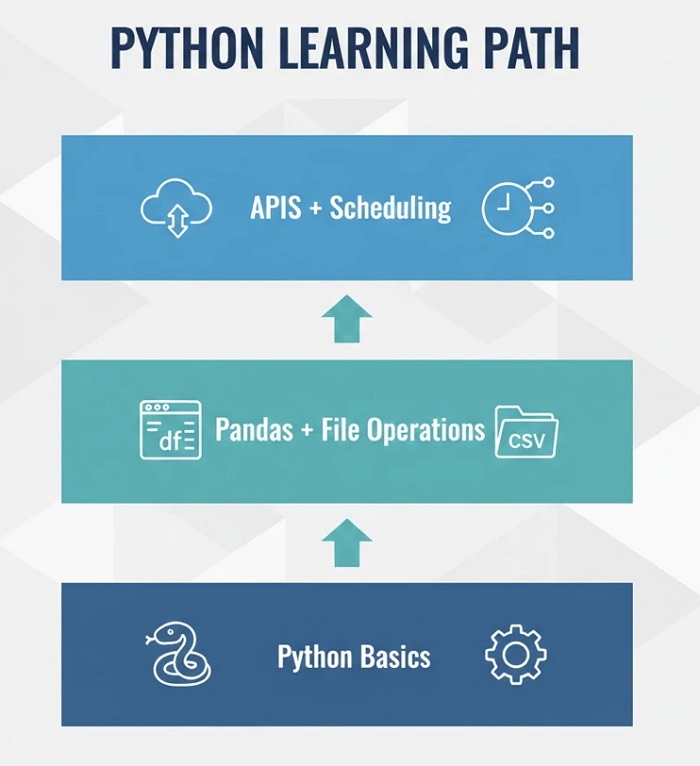
Python Fundamentals
Before automating anything, you need comfortable Python basics: variables, loops, functions, file handling, error handling. Don’t rush this — shaky fundamentals cause endless frustration later. Spend 4-6 weeks here until writing basic scripts feels natural.
Pandas for Data Manipulation
Pandas is the workhorse library for data automation. Reading Excel files, cleaning messy data, transforming columns, merging datasets, exporting results — pandas handles it all. Master the basics: DataFrames, filtering, grouping, and common operations like merge and pivot. This single library will power most of your automation work.
File Operations
Real automation means working with files constantly. Reading CSVs, writing Excel files, organizing folders, watching for new files, processing PDFs. Learn Python’s pathlib and os modules. Understand how to handle different encodings (the source of many headaches).
API Interactions
Modern data lives in cloud services accessed via APIs. Learn the requests library to pull data from web services, push updates to systems, and connect different platforms. Understanding JSON and basic HTTP concepts is essential.
Scheduling and Automation
Scripts that run manually aren’t truly automated. Learn to schedule Python scripts using cron (Mac/Linux) or Task Scheduler (Windows). Understand how to make scripts run reliably without supervision — logging, error notifications, handling edge cases.
Choosing the Right Python Automation Training
Courses range from free YouTube tutorials to expensive bootcamps. Here’s how to evaluate them:
Project-based learning: The best training builds real projects, not just explains concepts. You should finish with working automation scripts you can show employers or use immediately.
Data focus: General Python courses teach web development, games, and everything else. For data automation, look for training specifically covering pandas, Excel automation, API integration, and file processing.
Practical examples: Theoretical knowledge of pandas methods doesn’t help when facing messy real-world data. Good training shows how to handle actual problems — missing values, inconsistent formats, encoding errors.
Updated content: Python evolves. Courses from 2020 might teach outdated approaches. Look for recently updated material reflecting current best practices.
Community or support: Getting stuck is inevitable. Training with active forums, Discord communities, or instructor access helps you push through obstacles.
Common Mistakes When Learning
Avoid these pitfalls that trap many learners:
- Tutorial hell: Watching courses without building anything — start creating your own projects immediately
- Perfection paralysis: Waiting until you “know enough” — working code beats theoretical perfection
- Ignoring fundamentals: Jumping to pandas without solid Python basics causes endless frustration
- Learning in isolation: Share projects on GitHub, get feedback, join communities
Building Your Portfolio
Employers want proof you can deliver. Build projects demonstrating these abilities:
- Data cleaning: Transform a messy public dataset into clean format, documenting your process
- Report automation: Script that generates reports — pulling data, creating visualizations, exporting to Excel
- API integration: Connect multiple services — pull from one API, process, push to another
- File processing: Monitor folders, process new files automatically, organize results
From Learning to Earning
Python data automation skills translate directly to income. Entry-level automation specialists earn $55,000-$75,000. With experience, salaries reach $90,000-$120,000. Freelance automation projects command $50-$150 per hour depending on complexity.
The path is clear: learn fundamentals, build projects, demonstrate value, get hired. Companies need people who can automate their data headaches — and they’ll pay well for the solution.
Ready to start? The Python Automation Course covers exactly these skills — from Python basics through practical data automation projects you can use in your portfolio and career.